lv compaction | non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines lv compaction Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized . Available Online. 62 Article (s) Sort by. 30 Montaigne East-West Bag with Chain. $3,500.00. 30 Montaigne East-West Bag with Chain. $3,500.00. New. Small 30 Montaigne Bag. $3,600.00. Small 30 Montaigne Bag. $3,600.00. 30 Montaigne East-West Bag with Chain. $3,500.00. 30 Montaigne East-West Bag with Chain. $3,500.00.
0 · non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines
1 · non compaction cardiomyopathy echo criteria
2 · left ventricular non compaction symptoms
3 · compaction vs non cardiomyopathy
4 · bi ventricular non compaction cardiomyopathy
5 · Lv non compaction on echo
6 · Lv non compaction guidelines
7 · Lv compaction cardiomyopathy
In September 2017, Hurricane Irma struck Bahia Honda State Park and severely .
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized . Left ventricular noncompaction is a rare cardiomyopathy, that should be considered as a possible diagnosis because of its potential complications – heart failure, ventricular . Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer.
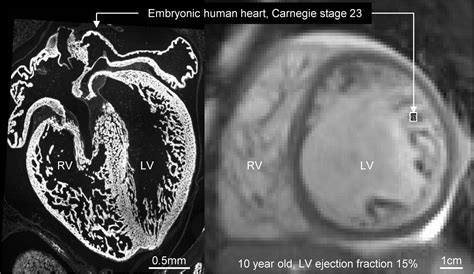
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [2,3].
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick. Left ventricular noncompaction is a rare cardiomyopathy, that should be considered as a possible diagnosis because of its potential complications – heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias, and embolic events.
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles published on LVNC has grown dramatically over the past decade.
Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy (LVNC): symptoms, diagnosis, and management options. Join our support group for guidance and information.Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare congenital phenotype defined by the presence of prominent left ventricular trabeculae, deep intertrabecular recesses (continuous with the ventricular cavity), and a thin compacted layer.Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a congenital pathology that directly affects the lining walls of myocardial tissue, causing trabeculations with blood filling in the inner wall of the heart, concomitantly with the development of a mesocardial thinning.
LVNC, also known as spongy myocardium, is a distinct form of cardiomyopathy occurring in-utero when segments of spongy myocardium fail to transform into compact, mature musculature resulting in prominent myocardial trabeculae, deep intra-trabecular recesses, and decreased cardiac function (1). There is considerable overlap between left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) and other cardiomyopathies. LVNC has been reported in up to 40% of the general population, raising questions about whether it is a distinct pathological entity, a remodeling epiphenomenon, or merely an anatomical phenotype. Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer.
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [2,3]. Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick. Left ventricular noncompaction is a rare cardiomyopathy, that should be considered as a possible diagnosis because of its potential complications – heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias, and embolic events.
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles published on LVNC has grown dramatically over the past decade.Left Ventricular Non-Compaction Cardiomyopathy (LVNC): symptoms, diagnosis, and management options. Join our support group for guidance and information.
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare congenital phenotype defined by the presence of prominent left ventricular trabeculae, deep intertrabecular recesses (continuous with the ventricular cavity), and a thin compacted layer.Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) is a congenital pathology that directly affects the lining walls of myocardial tissue, causing trabeculations with blood filling in the inner wall of the heart, concomitantly with the development of a mesocardial thinning. LVNC, also known as spongy myocardium, is a distinct form of cardiomyopathy occurring in-utero when segments of spongy myocardium fail to transform into compact, mature musculature resulting in prominent myocardial trabeculae, deep intra-trabecular recesses, and decreased cardiac function (1).
non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines
non compaction cardiomyopathy echo criteria
left ventricular non compaction symptoms
The Dior 30 Montaigne bag is a House icon made from the finest leathers and materials for a design that's unmistakably Dior. Explore the classic collection.
lv compaction|non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines